DeviceLink Profile
DeviceLink Profiles are an extension of the ICC creation process. During the ICC process, the input space, device independent space, and output color space typically do not match. Device profiles link input directly to output to avoid color issues between design and print. Device profiles replace the input and output profiles in your print mode.
Example:
| Input | Device Independent | Output |
|---|---|---|
| CMYK | Lab | CMYK |
|
RGB |
To create a DeviceLink Profile:
- Add a source profile.
- Add a target profile.
- Add a correction profile.
- Add a DeviceLink Profile Name.
- Use the table below for help, then click Finish.
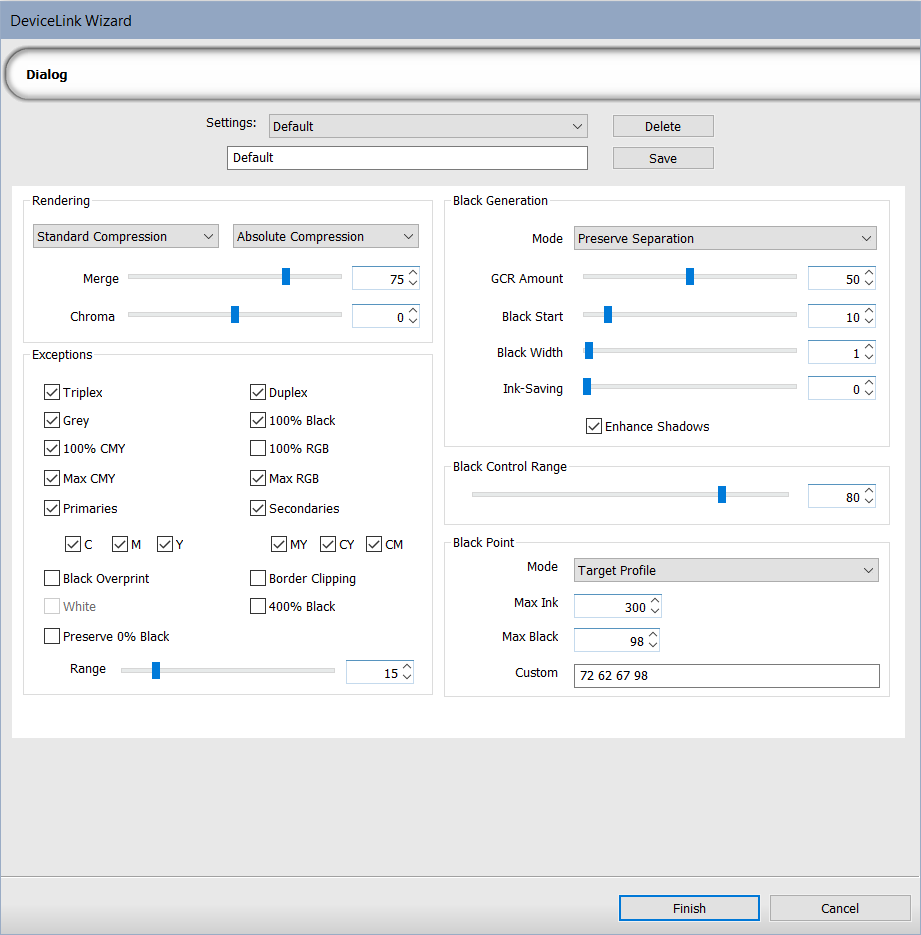
|
Settings |
|
|---|---|
| Default | Recommended. |
| Different Printer - Same Model | Use if you have the same model printer. |
| Large Format Printing | Use for large format printing. |
| MaxK + Pure Triplex + TAC From Profile | Use for maximum black, |
| Offset-to-Gravure | |
| Print-to-Print - GCR + Pure Triplex + TAC From Profile | |
| Print-to-Print - GCRmax240 + Pure Triplex | |
| Print-to-Print - Pure Triplex + TAC From Profile | |
| Print-to-Print - TAC330 + Pure Triplex | |
| Proofing | |
| Same Inks - Different Paper | |
| TAC Reduction - TAC300 | |
|
Save |
|
| Name field | Enter a name. |
| Delete and Save | With a setting selected, click Delete to remove it. With a name entered, click Save to save it. |
| Rendering | |
| Rendering Intent drop-down |
Select a rendering intent.
|
| Merge | Use the slider to merge the two selected rendering intents. |
| Chroma | Use the slider to increase or decrease the intensity (how intense the color is relative to the brightness of a white or illuminated area). |
| Exceptions | |
| Triplex (two primary colors plus black) |
Optimize the color conversion of a secondary color plus black to prevent contamination. Select to convert the triplex color to the most suitable color represented in the target color space consisting only of the triplex colors. Note: Contains exceptions: Duplex, Primaries, Secondaries, Gray, and 100% Black. |
| Duplex (a primary color plus black) |
Optimize the color conversion of a primary color plus black to prevent contamination. Select to convert the duplex color to the most suitable color represented in the target color space consisting only of the duplex colors. Note: Contains exceptions: Primaries, Secondaries, Gray, and 100% Black. |
| Gray |
Protects single-color structure of Black from 0% to 100%. For RGB, Gray ensures gray is composed of equal RGB value proportions. For conversion from RGB source to a CMYK target, Gray ensures gray is black only. Note: Contains exceptions: 100% Black, and White. |
| 100% Black |
Ensure black is always 100% K, 0% CMY. For conversion from RGB (0,0,0) to CMYK, ensures black is 100% K. |
| 100% C, M, Y | Ensure C, M, Y is always 100% C, M, Y after color conversion. |
| 100% R, G, B | Ensure R, G, B is always 100% R, G, B after color conversion. |
| Max C, M, Y | Maximum saturation of primary colors. |
| Max R, G, B |
Calculates the best color correct vale with the highest level of saturation. R, G, B corresponds to combinations MY, CY, and CM. Maximum saturation (100%) of the higher color value and the second color value is optimized colorimetrically. Note: To ensure 100% red remains 100% red, use 100% RGB. |
| Primaries |
Protects single-color structure of primary colors. Calculates the L*a*b value of source profile primary color and finds the best primary color match in the target profile. Note: When disabled, can cause color contamination of primaries in the target profile. Select individual primaries to allow protection of individual primaries. |
| Secondaries |
Protects the two-color structure of secondary colors. Calculates the L*a*b value of source profile secondary color and finds the best secondary color match in the target profile. Note: When disabled, can cause color contamination of secondaries in the target profile. Select individual secondaries to allow protection for individual secondaries. |
| Black Overprint | Protects 100% black (above a CMY background as an added layer). |
| Border Clipping | Any percentage value close to 0 is set to 0% and any value close to 100% is rounded to 100%, resulting in pure tones. |
| White |
Protects paper white. Use for absolute colorimetric simulation for proofing. |
| 400% Black | Protects 400% black absolutely. |
| Preserve 0% Black | Prevents a black channel from generating in source colors that do not include black. Can be used for overprints. |
| Range | Set a tolerance for adjacent color inclusion. |
|
Black Generation |
|
| Mode |
Select from the following options as a separation method:
Note: All calculations below are based on this selection. |
| GCR Amount |
Corresponds to the amount of black used instead of CMY; increasing the value increases the amount of black (at 100, black is linear). Lower values affect shadows and higher ranges affect light and dark areas. Note: Only available if Grey Component Replacement (GCR) mode is selected. |
| Black Start | Use the slider to control the black start. This is the point at which black is used once CMY passes the set value. Lower values correspond to no black. |
| Black Width |
Use the slider to control the black width. This is the range of values outside of the neutral area in which to generate black. Lower values correspond to less black being used as the width does not fall outside of the neutral zone. Higher values correspond to more black as the width falls outside of the neutral zone and more gray is visible. |
| Ink Saving | Use the slider to control the amount of ink saving. |
| Enhance Shadows | Details are preserved in dark colors and weak shadows. |
| Black Control Range |
Creates a smooth transition to black.
Note: The default value (80) is recommended. |
|
Black Point |
|
| Calculation Method |
Select from the following options:
|
| Max Ink Found | Displays maximum ink found based on tab settings. |
| Max Black Ink | The highest amount of black used to get a good black with ink jet printing. |
| Custom | Click to edit the values. |
