DeviceLink Profile (Perfil de vínculo con dispositivo)
Los Perfiles de dispositivo son una extensión del proceso de creación ICC. Durante el proceso ICC, el espacio de entrada, el espacio independiente del dispositivo y el espacio de color de salida normalmente no coinciden. Los perfiles de dispositivo unen la entrada directamente con la salida para evitar incidencias en color entre el diseño y la impresión. Los perfiles de dispositivo reemplazan los perfiles de entrada y salida en el modo de impresión.
Ejemplo:
| Entrada | Independiente de dispositivo | Salida |
|---|---|---|
| CMYK | LAB | CMYK |
|
RGB |
To create a DeviceLink Profile:
- Add a source profile.
- Add a target profile.
- Add a correction profile.
- Add a DeviceLink Profile Name.
- Utilice la siguiente tabla como ayuda, después haga clic en Finalizar.
|
Ajustes |
|
|---|---|
| Predeterminado | Recommended. |
| Different Printer - Same Model | Use if you have the same model printer. |
| Large Format Printing | Use for large format printing. |
| MaxK + Pure Triplex + TAC From Profile | Use for maximum black, |
| Offset-to-Gravure | |
| Print-to-Print - GCR + Pure Triplex + TAC From Profile | |
| Print-to-Print - GCRmax240 + Pure Triplex | |
| Print-to-Print - Pure Triplex + TAC From Profile | |
| Print-to-Print - TAC330 + Pure Triplex | |
| Proofing | |
| Same Inks - Different Paper | |
| TAC Reduction - TAC300 | |
|
Guardar |
|
| Name field | Introduzca un nombre. |
| Delete and Save | With a setting selected, click Delete to remove it. With a name entered, click Save to save it. |
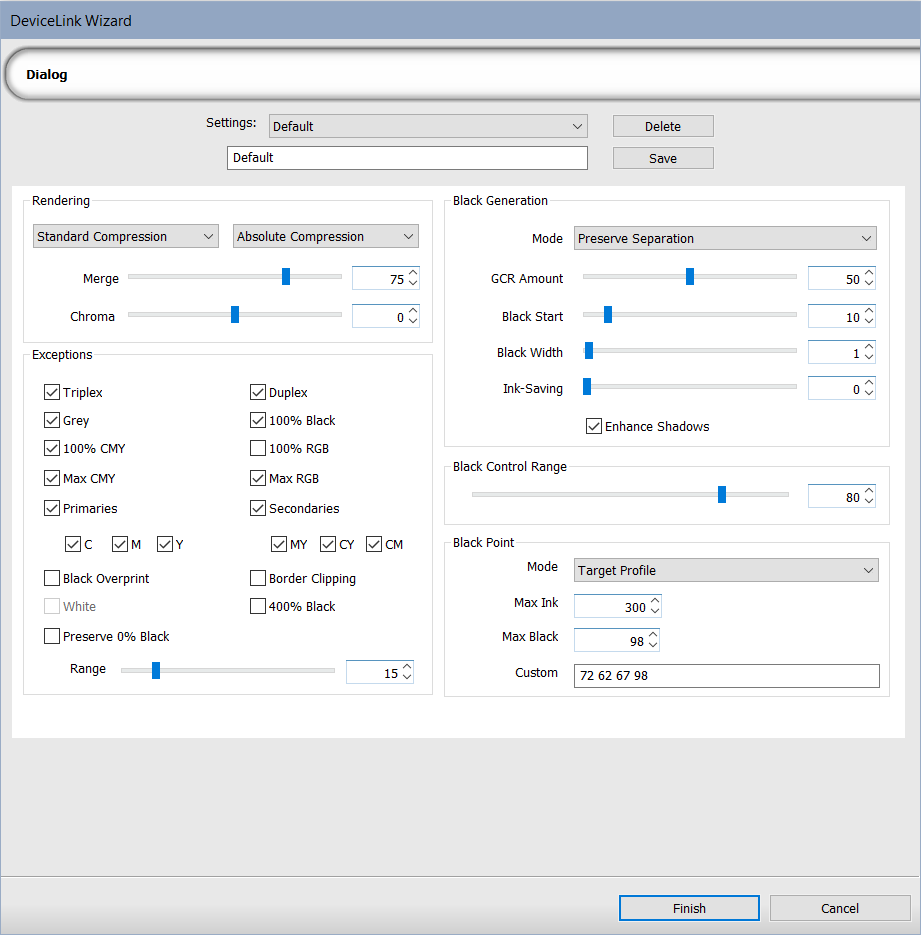
| Representación | |
| Rendering Intent drop-down |
Select a rendering intent.
|
| Merge | Use the slider to merge the two selected rendering intents. |
| Croma | Use the slider to increase or decrease the intensity (how intense the color is relative to the brightness of a white or illuminated area). |
| Exceptions | |
| Triplex (two primary colors plus black) |
Optimize the color conversion of a secondary color plus black to prevent contamination. Select to convert the triplex color to the most suitable color represented in the target color space consisting only of the triplex colors. Note: Contains exceptions: Duplex, Primaries, Secondaries, Gray, and 100% Black. |
| Duplex (a primary color plus black) |
Optimize the color conversion of a primary color plus black to prevent contamination. Select to convert the duplex color to the most suitable color represented in the target color space consisting only of the duplex colors. Note: Contains exceptions: Primaries, Secondaries, Gray, and 100% Black. |
| Gray |
Protects single-color structure of Black from 0% to 100%. For RGB, Gray ensures gray is composed of equal RGB value proportions. For conversion from RGB source to a CMYK target, Gray ensures gray is black only. Note: Contains exceptions: 100% Black, and White. |
| 100% Black |
Ensure black is always 100% K, 0% CMY. For conversion from RGB (0,0,0) to CMYK, ensures black is 100% K. |
| 100% C, M, Y | Ensure C, M, Y is always 100% C, M, Y after color conversion. |
| 100% R, G, B | Ensure R, G, B is always 100% R, G, B after color conversion. |
| Max C, M, Y | Maximum saturation of primary colors. |
| Max R, G, B |
Calculates the best color correct vale with the highest level of saturation. R, G, B corresponds to combinations MY, CY, and CM. Maximum saturation (100%) of the higher color value and the second color value is optimized colorimetrically. Note: To ensure 100% red remains 100% red, use 100% RGB. |
| Primaries |
Protects single-color structure of primary colors. Calculates the L*a*b value of source profile primary color and finds the best primary color match in the target profile. Note: When disabled, can cause color contamination of primaries in the target profile. Select individual primaries to allow protection of individual primaries. |
| Secondaries |
Protects the two-color structure of secondary colors. Calculates the L*a*b value of source profile secondary color and finds the best secondary color match in the target profile. Note: When disabled, can cause color contamination of secondaries in the target profile. Select individual secondaries to allow protection for individual secondaries. |
| Black Overprint | Protects 100% black (above a CMY background as an added layer). |
| Border Clipping | Any percentage value close to 0 is set to 0% and any value close to 100% is rounded to 100%, resulting in pure tones. |
| White |
Protects paper white. Use for absolute colorimetric simulation for proofing. |
| 400% Black | Protects 400% black absolutely. |
| Conservar un 0 % de negro | Prevents a black channel from generating in source colors that do not include black. Can be used for overprints. |
| Range | Set a tolerance for adjacent color inclusion. |
|
Pestaña de Generación de negro |
|
| Modo |
Seleccione de las opciones siguientes como un método de separación:
Nota: Todas los cálculos siguientes se basan en esta selección. |
| Cantidad GCR |
Corresponde a la cantidad de negro usado en lugar de CMY; aumentando el valor que aumenta la cantidad de negro (con 100, el negro es lineal). Los valores más bajos afectan a la sombra y los intervalos más altos afectan a las zonas oscuras y luminosas. Nota: Solo disponible si se selecciona el modo Reemplazo de componente gris (GCR). |
| Inicio en negro | Utilice el control deslizante para controlar el inicio en negro. Este es el punto en el que se usará negro una vez que el CMY supere el valor establecido. Los valores más bajos representan la falta de negro. |
| Amplitud de negro |
Utilice el control deslizante para ajustar la amplitud de negro. Esto indica el rango de valores fuera del área neutra en la que generar negro. Los valores más bajos indican menos negro usado ya que la amplitud no se sitúa fuera de la zona neutra. Los valores más altos indican más negro, ya que la amplitud se sitúa fuera de la zona neutra y puede verse más gris. |
| Ahorro de tinta | Use the slider to control the amount of ink saving. |
| Enhance Shadows | Details are preserved in dark colors and weak shadows. |
| Black Control Range |
Creates a smooth transition to black.
Note: The default value (80) is recommended. |
|
Punto negro |
|
| Método de cálculo |
Seleccione entre las siguientes opciones:
|
| Tinta máx. encontrada | Muestra la tinta máxima encontrada según los ajustes de la pestaña. |
| Tinta negra máx. | La cantidad más elevada de negro usada para obtener un buen negro con impresión de inyección de tinta. |
| Personalizado | Click to edit the values. |
