Note: These materials are offered only in English as supplementary examples for a deeper dive into
Rendering Dialog
The Rendering dialog allows you to select rendering intents, merge intents, set chroma, and select rendering exceptions.
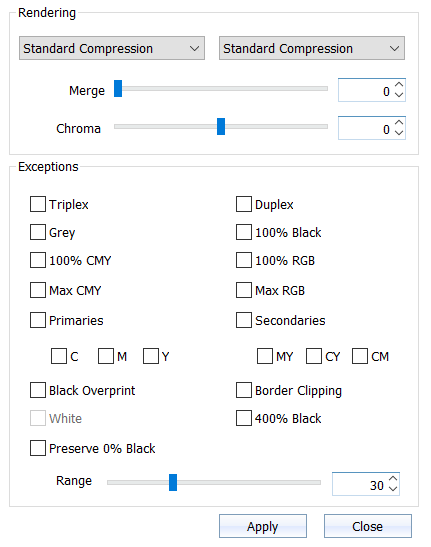
| Rendering | |
|---|---|
| Rendering Intent drop-down |
Select a rendering intent. The first four rendering intents are defined by the ICC Consortium. Perceptual Profiles created with different programs may be different, especially with smaller gamuts.
Corlorimetric Profiles created with different programs will create
The following rendering intents are not recommended for DTG printing.
The following two rendering intents are useful for blending rendering intents. These are equivalent but not exactly the same as the intents above (Relative and Absolute). Note: Used for blending rendering intents.
|
| Merge | Use the slider to merge the two selected rendering intents. |
| Chroma | Use the slider to increase or decrease the intensity (how intense the color is relative to the brightness of a white or illuminated area). |
| Exceptions | |
| Triplex (two primary colors plus black) |
Optimize the color conversion of a secondary color plus black to prevent contamination. Select to convert the triplex color to the most suitable color represented in the target color space consisting only of the triplex colors. Note: Contains exceptions: Duplex, Primaries, Secondaries, Gray, and 100% Black. |
| Duplex (a primary color plus black) |
Optimize the color conversion of a primary color plus black to prevent contamination. Select to convert the duplex color to the most suitable color represented in the target color space consisting only of the duplex colors. Note: Contains exceptions: Primaries, Secondaries, Gray, and 100% Black. |
| Gray |
Protects single-color structure of Black from 0% to 100%. For RGB, Gray ensures gray is composed of equal RGB value proportions. For conversion from RGB source to a CMYK target, Gray ensures gray is black only. Note: Contains exceptions: 100% Black, and White. |
| 100% Black |
Ensure black is always 100% K, 0% CMY. For conversion from RGB (0,0,0) to CMYK, ensures black is 100% K. |
| 100% C, M, Y | Ensure C, M, Y is always 100% C, M, Y after color conversion. |
| 100% R, G, B | Ensure R, G, B is always 100% R, G, B after color conversion. |
| Max C, M, Y | Maximum saturation of primary colors. |
| Max R, G, B |
Calculates the best color correct vale with the highest level of saturation. R, G, B corresponds to combinations MY, CY, and CM. Maximum saturation (100%) of the higher color value and the second color value is optimized colorimetrically. Note: To ensure 100% red remains 100% red, use 100% RGB. |
| Primaries |
Protects single-color structure of primary colors. Calculates the L*a*b value of source profile primary color and finds the best primary color match in the target profile. Note: When disabled, can cause color contamination of primaries in the target profile. Select individual primaries to allow protection of individual primaries. |
| Secondaries |
Protects the two-color structure of secondary colors. Calculates the L*a*b value of source profile secondary color and finds the best secondary color match in the target profile. Note: When disabled, can cause color contamination of secondaries in the target profile. Select individual secondaries to allow protection for individual secondaries. |
| Black Overprint | Protects 100% black (above a CMY background as an added layer). |
| Border Clipping | Any percentage value close to 0 is set to 0% and any value close to 100% is rounded to 100%, resulting in pure tones. |
| White |
Protects paper white. Use for absolute colorimetric simulation for proofing. |
| 400% Black | Protects 400% black absolutely. |
| Preserve 0% Black | Prevents a black channel from generating in source colors that do not include black. Can be used for overprints. |
| Range | Set a tolerance for adjacent color inclusion. |
